Juvenile Gingivitis In Cats

Periodontal disease is common in feline practice.
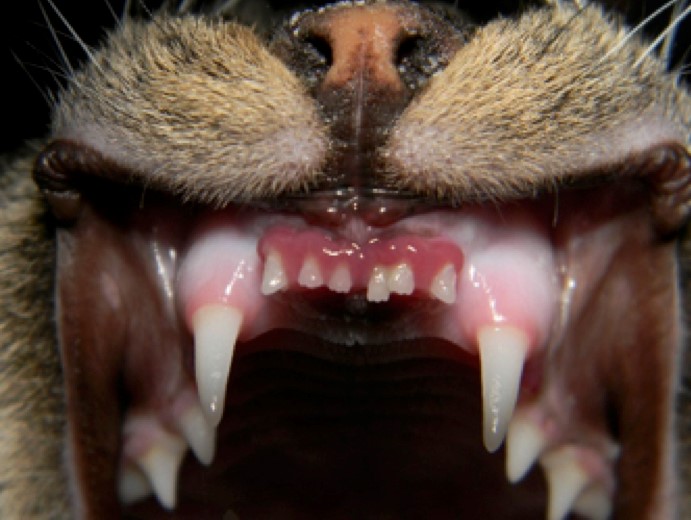
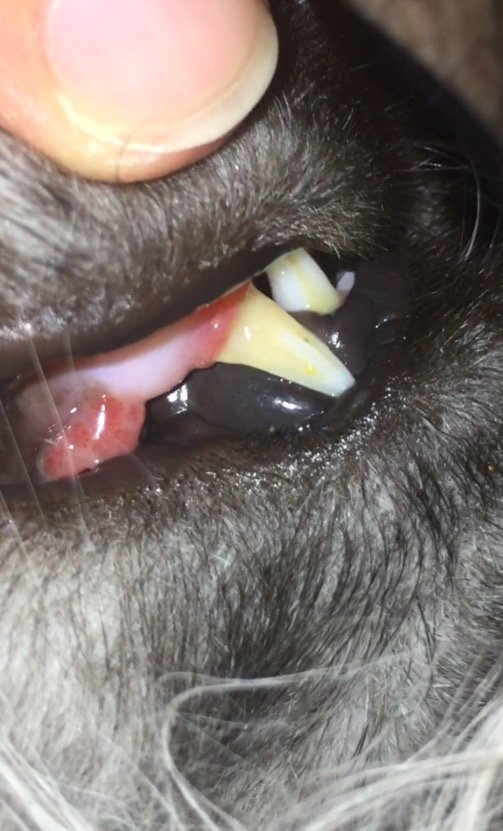
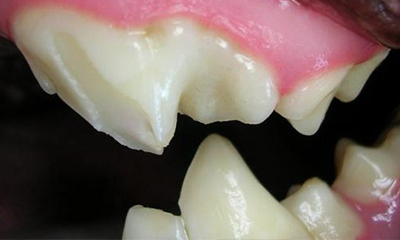
Juvenile gingivitis in cats. Causes may include exaggerated inflammation at the time of tooth eruption viral exposure felv fiv calici immune mediated disorders or mixture of reasons. There is a pronounced inflammation of the gingiva often followed by marked hyperplasia of the tissue. Feline juvenile gingivitis some immature cats display pronounced inflammation of the gums that has not spread to the back of the mouth called feline juvenile gingivitis. Gingivitis juvenile onset periodontitis stomatitis tooth resorption or a combination.
One of these conditions is called juvenile onset periodontitis. Juvenile gingivitis is typically diagnosed between 6 and 12 months of age. There are also subsets of oral disease that can affect the young or juvenile feline patient. Juvenile feline hyperplastic gingivitis is a pronounced generalized inflammation and overproduction of the attached gingival gum tissues in the young cat.
Juvenile onset feline gingivitis periodontitis is a form of periodontal disease occasionally seen in cats less than 1 year of age. Feline juvenile gingivitis aka juvenile hyperplastic gingivitis is a pronounced generalized inflammation of the gingival tissues in the young cat. Onset of inflammation can be as early as the time of eruption of the permanent teeth. In these patients intense gingivitis may begin at the time of tooth eruption progressing to read more about feline juvenile onset.
Figure 1 it is typically diagnosed around the time of tooth eruption between 7 10 months of age. This cat gum disease is similar to a condition called aggressive periodontitis which is seen in humans during the teenage years.